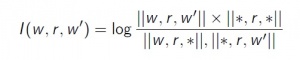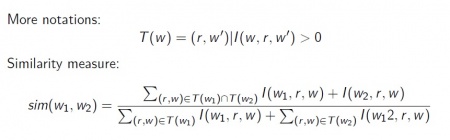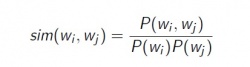Lecture 6. Synonyms and near-synonyms detection — различия между версиями
Polidson (обсуждение | вклад) (→Dependency triple [Lin, 1998]) |
Polidson (обсуждение | вклад) (→Web or corpus search approach) |
||
| Строка 99: | Строка 99: | ||
=== Web or corpus search approach === | === Web or corpus search approach === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Hearst patterns [Hearst, 1998] ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lexico-syntactic patterns to recognize hyponymy: | ||
| + | * such NP as NP, NP and / or NP; | ||
| + | * NP such as NP, NP and / or NP; | ||
| + | * NP, NP or other NP; | ||
| + | * NP, NP and other NP; | ||
| + | * NP, including NP, NP and / or NP; | ||
| + | * NP, especially NP, NP and / or NP; | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Text ⇒ pattern ⇒ concordance | ||
| + | |||
| + | To rank concordances: PatternSim [Panchenko, Morozova, Naets] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Concordance ranking: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Input: Terms C, Corpus D | ||
| + | |||
| + | Output: Similarity matrix S(C x C) | ||
| + | |||
| + | K ← extract concord(D); | ||
| + | |||
| + | K<sub>lem </sub> ← lemmatize concord(K); | ||
| + | |||
| + | KC ← filter concord(Klem; C); | ||
| + | |||
| + | S ← get extractionfreq(C;K); | ||
| + | |||
| + | S ← rerank(S; C;D); | ||
| + | |||
| + | S ← normalize(S); | ||
| + | |||
| + | return S | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example ranking '''Efreq-Cfreq''': | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Файл:L6p4.jpg|250px|слева]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> <br> <br> <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | P(w<sub>i</sub>) — frequency of (w<sub>i</sub>) P(w<sub>i</sub>, w<sub>j</sub>) — extraction probability of (w<sub>i</sub>,w<sub>j</sub>) | ||
| + | demo: [http://serelex.cental.be/|http://serelex.cental.be/] | ||
Версия 03:41, 3 сентября 2015
Содержание
Examples
- Synonyms: Netherlands and Holland, buy and purchase
- Near synonyms: pants, trousers and slacks, mistake and error
Approaches to synonyms and near-synonyms detection
- Thesaurus-based approach
- Distributional semantics
- Context-based approach
- word2vec
- Web search-based approach
Synonyms in WordNet
Given a word, look for synonyms in every synset.
WordNet NLTK interface
In[1]: for i,j in enumerate(wn.synsets('error')):
In[2]: print "Meaning",i, "NLTK ID:", j.name()
In[3]: print "Definition:",j.definition()
In[4]: print "Synonyms:", ", ".join(j.lemma names())
Wordnet Web interface: [1]
Distributional semantics
Exercise 6.1
Calculate PPMI for Table 1.
Exercise 6.2
Input: def.txt or your own text
Output 1: term-context matrix
Output 2: term-term similarity matrix (use cosine similarity)
Output 3: 2D visualization by means of LSA
Hint: use cfd = nltk.ConditionalFreqDist((term, context) for ...) for computing conditional frequency dictionary
Hint: use R for SVD and visualization
word2vec [Mikolov, Chen, Corrado, Dean, 2013]
Very complex machine learning (deep learning) applied to term-context matrices.
There are two regimes:
- CBOW predicts the current word based on the context
- Skip-gram predicts surrounding words given the current word
word2vec project page: [2] demo: [3]
Example: vec(Madrid) - vec(Spain) + vec(France) = vec(Paris)
Context-based approach (1) [Lin, 1998]
Dependency triple [Lin, 1998]
A dependency triple (w, r, w') consists of two words and the grammatical relationship between them in the input sentence.
I have a brown dog: (have subj I), (I subj-of have), (dog obj-of have), (dog adj-mod brown), (brown adj-mod-of dog), (dog det a), (a det-of dog)
||w, r, w'|| — frequency of (w, r, w')
||w, r, * || — total occurrences of w-r relationships
|| *, *, *|| — total number of dependency triples
Mutual information between w, w':
Results: brief(noun) — affidavit 0.13, petition 0.05, memo-randum 0.05, motion 0.05, lawsuit 0.05, depo-sition 0.05, slight 0.05, prospectus 0.04, docu-ment 0.04 paper 0.04
- some sort of dependency parsing is required
- no difference between synonyms and antonyms (win / loose the game)
Web or corpus search approach
Hearst patterns [Hearst, 1998]
Lexico-syntactic patterns to recognize hyponymy:
- such NP as NP, NP and / or NP;
- NP such as NP, NP and / or NP;
- NP, NP or other NP;
- NP, NP and other NP;
- NP, including NP, NP and / or NP;
- NP, especially NP, NP and / or NP;
Text ⇒ pattern ⇒ concordance
To rank concordances: PatternSim [Panchenko, Morozova, Naets]
Concordance ranking:
Input: Terms C, Corpus D
Output: Similarity matrix S(C x C)
K ← extract concord(D);
Klem ← lemmatize concord(K);
KC ← filter concord(Klem; C);
S ← get extractionfreq(C;K);
S ← rerank(S; C;D);
S ← normalize(S);
return S
Example ranking Efreq-Cfreq:
P(wi) — frequency of (wi) P(wi, wj) — extraction probability of (wi,wj) demo: [4]